Better sleep habits lead to better college grades
Data on MIT students underscore the importance of getting enough sleep; bedtime also matters.
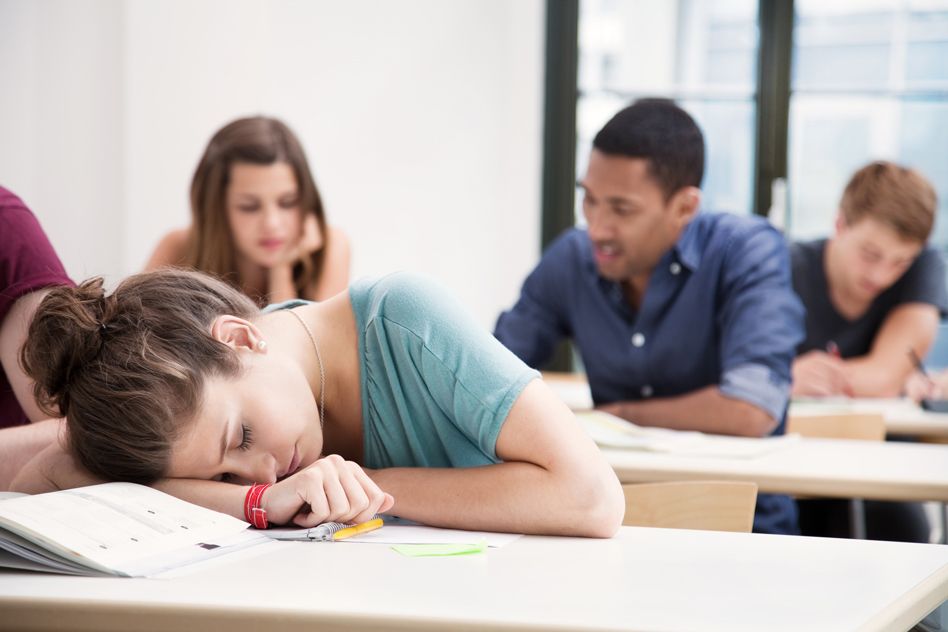

Two MIT professors have found a strong relationship between students’ grades and how much sleep they’re getting. What time students go to bed and the consistency of their sleep habits also make a big difference. And no, getting a good night’s sleep just before a big test is not good enough — it takes several nights in a row of good sleep to make a difference.
Those are among the conclusions from an experiment in which 100 students in an MIT engineering class were given Fitbits, the popular wrist-worn devices that track a person’s activity 24/7, in exchange for the researchers’ access to a semester’s worth of their activity data. The findings — some unsurprising, but some quite unexpected — are reported today in the journal Science of Learning in a paper by former MIT postdoc Kana Okano, professors Jeffrey Grossman and John Gabrieli, and two others.
One of the surprises was that individuals who went to bed after some particular threshold time — for these students, that tended to be 2 a.m., but it varied from one person to another — tended to perform less well on their tests no matter how much total sleep they ended up getting.
The study didn’t start out as research on sleep at all. Instead, Grossman was trying to find a correlation between physical exercise and the academic performance of students in his class 3.091 (Introduction to Solid-State Chemistry). In addition to having 100 of the students wear Fitbits for the semester, he also enrolled about one-fourth of them in an intense fitness class in MIT’s Department of Athletics, Physical Education, and Recreation, with the help of assistant professors Carrie Moore and Matthew Breen, who created the class specifically for this study. The thinking was that there might be measurable differences in test performance between the two groups.
There wasn’t. Those without the fitness classes performed just as well as those who did take them. “What we found at the end of the day was zero correlation with fitness, which I must say was disappointing since I believed, and still believe, there is a tremendous positive impact of exercise on cognitive performance,” Grossman says.
He speculates that the intervals between the fitness program and the classes may have been too long to show an effect. But meanwhile, in the vast amount of data collected during the semester, some other correlations did become obvious. While the devices weren’t explicitly monitoring sleep, the Fitbit program’s proprietary algorithms did detect periods of sleep and changes in sleep quality, primarily based on lack of activity.
These correlations were not at all subtle, Grossman says. There was essentially a straight-line relationship between the average amount of sleep a student got and their grades on the 11 quizzes, three midterms, and final exam, with the grades ranging from A’s to C’s. “There’s lots of scatter, it’s a noisy plot, but it’s a straight line,” he says. The fact that there was a correlation between sleep and performance wasn’t surprising, but the extent of it was, he says. Of course, this correlation can’t absolutely prove that sleep was the determining factor in the students’ performance, as opposed to some other influence that might have affected both sleep and grades. But the results are a strong indication, Grossman says, that sleep “really, really matters.”
“Of course, we knew already that more sleep would be beneficial to classroom performance, from a number of previous studies that relied on subjective measures like self-report surveys,” Grossman says. “But in this study the benefits of sleep are correlated to performance in the context of a real-life college course, and driven by large amounts of objective data collection.”
The study also revealed no improvement in scores for those who made sure to get a good night’s sleep right before a big test. According to the data, “the night before doesn’t matter,” Grossman says. “We’ve heard the phrase ‘Get a good night’s sleep, you’ve got a big day tomorrow.’ It turns out this does not correlate at all with test performance. Instead, it’s the sleep you get during the days when learning is happening that matter most.”
Another surprising finding is that there appears to be a certain cutoff for bedtimes, such that going to bed later results in poorer performance, even if the total amount of sleep is the same. “When you go to bed matters,” Grossman says. “If you get a certain amount of sleep — let’s say seven hours — no matter when you get that sleep, as long as it’s before certain times, say you go to bed at 10, or at 12, or at 1, your performance is the same. But if you go to bed after 2, your performance starts to go down even if you get the same seven hours. So, quantity isn’t everything.”
Quality of sleep also mattered, not just quantity. For example, those who got relatively consistent amounts of sleep each night did better than those who had greater variations from one night to the next, even if they ended up with the same average amount.
This research also helped to provide an explanation for something that Grossman says he had noticed and wondered about for years, which is that on average, the women in his class have consistently gotten better grades than the men. Now, he has a possible answer: The data show that the differences in quantity and quality of sleep can fully account for the differences in grades. “If we correct for sleep, men and women do the same in class. So sleep could be the explanation for the gender difference in our class,” he says.
More research will be needed to understand the reasons why women tend to have better sleep habits than men. “There are so many factors out there that it could be,” Grossman says. “I can envision a lot of exciting follow-on studies to try to understand this result more deeply.”
“The results of this study are very gratifying to me as a sleep researcher, but are terrifying to me as a parent,” says Robert Stickgold, a professor of psychiatry and director of the Center for Sleep and Cognition at Harvard Medical School, who was not connected with this study. He adds, “The overall course grades for students averaging six and a half hours of sleep were down 50 percent from other students who averaged just one hour more sleep. Similarly, those who had just a half-hour more night-to-night variation in their total sleep time had grades that dropped 45 percent below others with less variation. This is huge!”
Stickgold says “a full quarter of the variation in grades was explained by these sleep parameters (including bedtime). All students need to not only be aware of these results, but to understand their implication for success in college. I can’t help but believe the same is true for high school students.” But he adds one caution: “That said, correlation is not the same as causation. While I have no doubt that less and more variable sleep will hurt a student’s grades, it’s also possible that doing poorly in classes leads to less and more variable sleep, not the other way around, or that some third factor, such as ADHD, could independently lead to poorer grades and poorer sleep.”
The team also included technical assistant Jakub Kaezmarzyk and Harvard Business School researcher Neha Dave. The study was supported by MIT’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering, the Lubin Fund, and the MIT Integrated Learning Initiative.