Brain biomarkers predict mood and attention symptoms
Researchers find signatures in the young brain can be linked to future attentional and affective symptoms.

Mood and attentional disorders amongst teens are an increasing concern, for parents, society, and for peers. A recent Pew research center survey found conditions such as depression and anxiety to be the number one concern that young students had about their friends, ranking above drugs or bullying.
“We’re seeing an epidemic in teen anxiety and depression,” explains McGovern Research Affiliate Susan Whitfield-Gabrieli.
“Scientists are finding a huge increase in suicide ideation and attempts, something that hit home for me as a mother of teens. Emergency rooms in hospitals now have guards posted outside doors of these teenagers that attempted suicide—this is a pressing issue,” explains Whitfield-Gabrieli who is also director of the Northeastern University Biomedical Imaging Center and a member of the Poitras Center for Psychiatric Disorders Research.
Finding new methods for discovering early biomarkers for risk of psychiatric disorders would allow early interventions and avoid reaching points of crisis such as suicide ideation or attempts. In research published recently in JAMA Psychiatry, Whitfield-Gabrieli and colleagues found that signatures predicting future development of depression and attentional symptoms can be detected in children as young as seven years old.
Long-term view
While previous work had suggested that there may be biomarkers that predict development of mood and attentional disorders, identifying early biomarkers prior to an onset of illness requires following a cohort of pre-teens from a young age, and monitoring them across years. This effort to have a proactive, rather than reactive, approach to the development of symptoms associated with mental disorders is exactly the route Whitfield-Gabrieli and colleagues took.
“One of the exciting aspects of this study is that the cohort is not pre-selected for already having symptoms of psychiatric disorders themselves or even in their family,” explained Whitfield-Gabrieli. “It’s an unbiased cohort that we followed over time.”
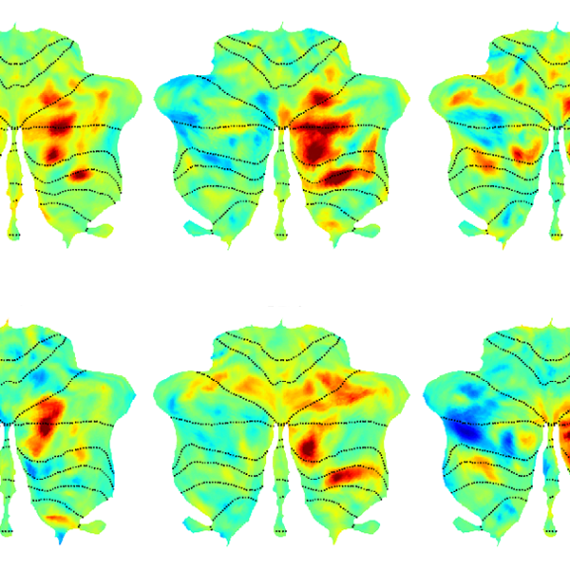
In some past studies, children were pre-selected, for example a major depressive disorder diagnosis in the parents, but Whitfield-Gabrieli and colleagues, Silvia Bunge from Berkeley and Laurie Cutting from Vanderbilt, recruited a range of children without preconditions, and examined them at age 7, then again 4 years later. The researchers examined resting state functional connectivity, and compared this to scores on the child behavioral checklist (CBCL), allowing them to relate differences in the brain to a standardized analysis of behavior that can be linked to psychiatric disorders. The CBCL is used both in research and in the clinic and his highly predictive of disorders including ADHD, so that changes in the brain could be related to changes in a widely used clinical scoring system.
“Over the four years, some people got worse, some got better, and some stayed the same according the CBCL. We could relate this directly to differences in brain networks, and could identify at age 7 who would get worse,” explained Whitfield-Gabrieli.
Brain network changes
The authors analyzed differences in resting state network connectivity, regions across the brain that rise and fall in activity level together, as visualized using fMRI. Reduced connectivity between these regions may allow us to get a handle on reduced “top-down” control of neural circuits. The dorsolateral prefrontal region is linked to executive function, external attention, and emotional control. Increased connection with the medial prefrontal cortex is known to be present in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), while a reduced connection to a different brain region, the sgACC, is seen in major depressive disorder. The question remained as to whether these changes can be seen prior to the onset of diagnosable attentional or mood disorders.
Whitfield-Gabrieli and colleagues found that these resting state networks varied in the brains of children that would later develop anxiety/depression and ADHD symptoms. Weaker scores in connectivity between the dorsolateral and medial prefrontal cortical regions tended to be seen in children whose attention scores went on to improve. Analysis of the resting state networks above could differentiate those who would have typical attentional behavior by age 11 versus those that went on to develop ADHD.
Whitfield-Gabrieli has replicated this finding in an independent sample of children and she is continuing to expand the analysis and check the results, as well as follow this cohort into the future. Should changes in resting state networks be a consistent biomarker, the next step is to initiate interventions prior to the point of crisis.
“We’ve recently been able to use mindfulness interventions, and show these reduce self-perceived stress and amygdala activation in response to fear, and we are also testing the effect of exercise interventions,” explained Whitfield-Gabrieli. “The hope is that by using predictive biomarkers we can augment children’s lifestyles with healthy interventions that can prevent risk converting to a psychiatric disorder.”