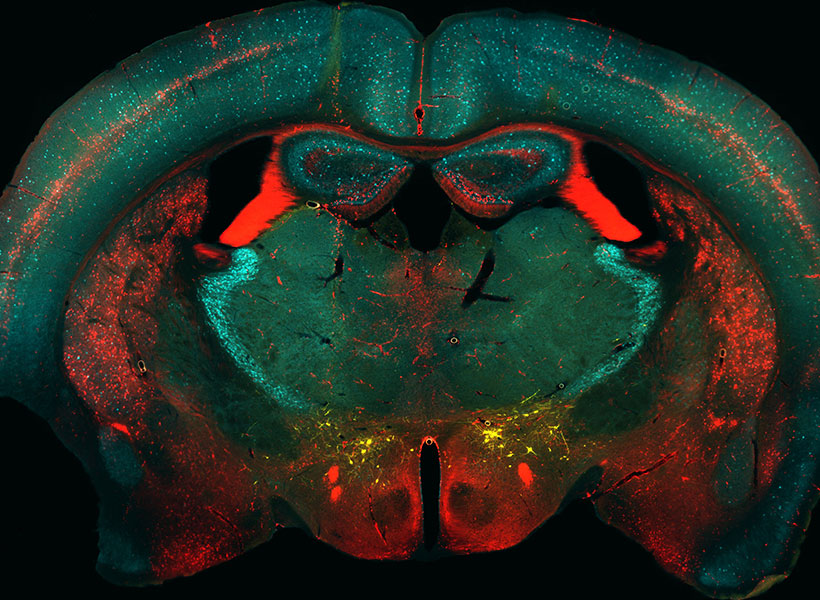
A new tool developed by researchers at MIT’s McGovern Institute gives neuroscientists the power to find connected neurons within the brain’s tangled network of cells, and then follow or manipulate those neurons over a prolonged period. Its development, led by Principal Research Scientist Ian Wickersham, transforms a powerful tool for exploring the anatomy of the brain into a sophisticated system for studying brain function.
Wickersham and colleagues have designed their system to enable long-term analysis and experiments on groups of neurons that reach through the brain to signal to select groups of cells. It is described in the January 11, 2024, issue of the journal Nature Neuroscience. “This second-generation system will allow imaging, recording, and control of identified networks of synaptically-connected neurons in the context of behavioral studies and other experimental designs lasting weeks, months, or years,” Wickersham says.
The system builds on an approach to anatomical tracing that Wickersham developed in 2007, as a graduate student in Edward Callaway’s lab at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies. Its key is a modified version of a rabies virus, whose natural—and deadly—life cycle involves traveling through the brain’s neural network.
Viral tracing
The rabies virus is useful for tracing neuronal connections because once it has infected the nervous system, it spreads through the neural network by co-opting the very junctions that neurons use to communicate with one another. Hopping across those junctions, or synapses, the virus can pass from cell to cell. Traveling in the opposite direction of neuronal signals, it reaches the brain, where it continues to spread.
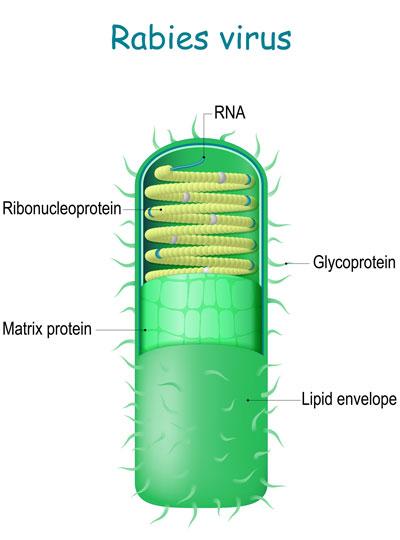
To use the rabies virus to identify specific connections within the brain, Wickersham modified it to limit its spread. His original tracing system uses a rabies virus that lacks an essential gene. When researchers deliver the modified virus to the neurons whose connections they want to map, they also instruct those neurons to make the protein encoded by the virus’s missing gene. That allows the virus to replicate and travel across the synapses that link an infected cell to others in the network. Once it is inside a new cell, the virus is deprived of the critical protein and can go no farther.
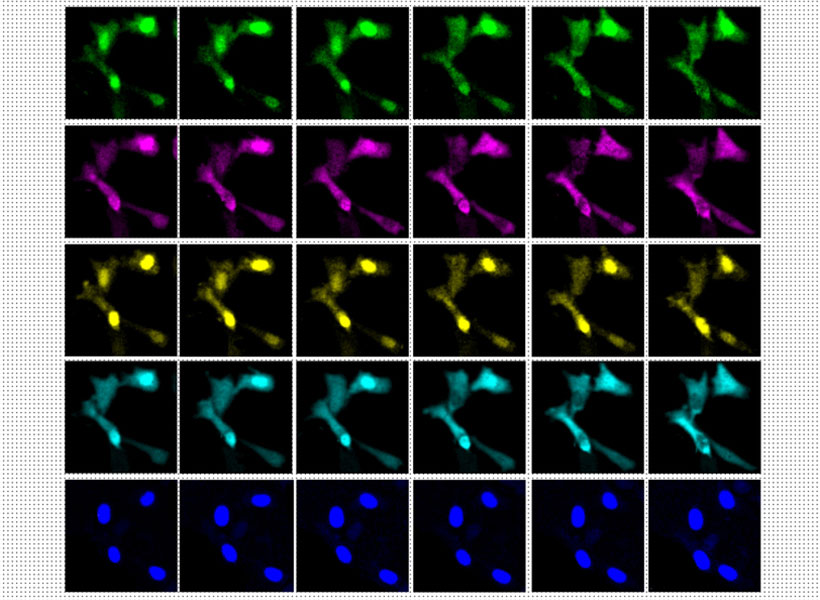
Under a microscope, a fluorescent protein delivered by the modified virus lights up, exposing infected cells: those to which the virus was originally delivered as well as any neurons that send it direct inputs. Because the virus crosses only one synapse after leaving the cell it originally infected, the technique is known as monosynaptic tracing.
Labs around the world now use this method to identify which brain cells send signals to a particular set of neurons. But while the virus used in the original system can’t spread through the brain like a natural rabies virus, it still sickens the cells it does infect. Infected cells usually die in about two weeks, and that has limited scientists’ ability to conduct further studies of the cells whose connections they trace. “If you want to then go on to manipulate those connected populations of cells, you have a very short time window,” Wickersham says.
Reducing toxicity
To keep cells healthy after monosynaptic tracing, Wickersham, postdoctoral researcher Lei Jin, and colleagues devised a new approach. They began by deleting a second gene from the modified virus they use to label cells. That gene encodes an enzyme the rabies virus needs to produce the proteins encoded in its own genome. As with the original system, neurons are instructed to create the virus’s missing proteins, equipping the virus to replicate inside those cells. In this case, this is done in mice that have been genetically modified to produce the second deleted viral gene in specific sets of neurons.
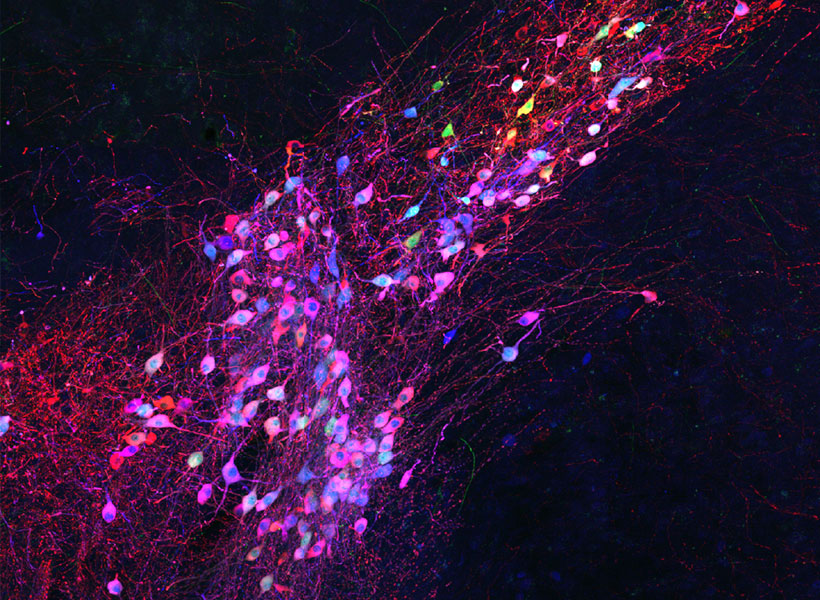
To limit toxicity, Wickersham and his team built in a control that allows researchers to switch off cells’ production of viral proteins once the virus has had time to replicate and begin its spread to connected neurons. With those proteins no longer available to support the viral life cycle, the tracing tool is rendered virtually harmless. After following mice for up to 10 weeks, the researchers detected minimal toxicity in neurons where monosynaptic tracing was initiated. And, Wickersham says, “as far as we can tell, the trans-synaptically labeled cells are completely unscathed.”
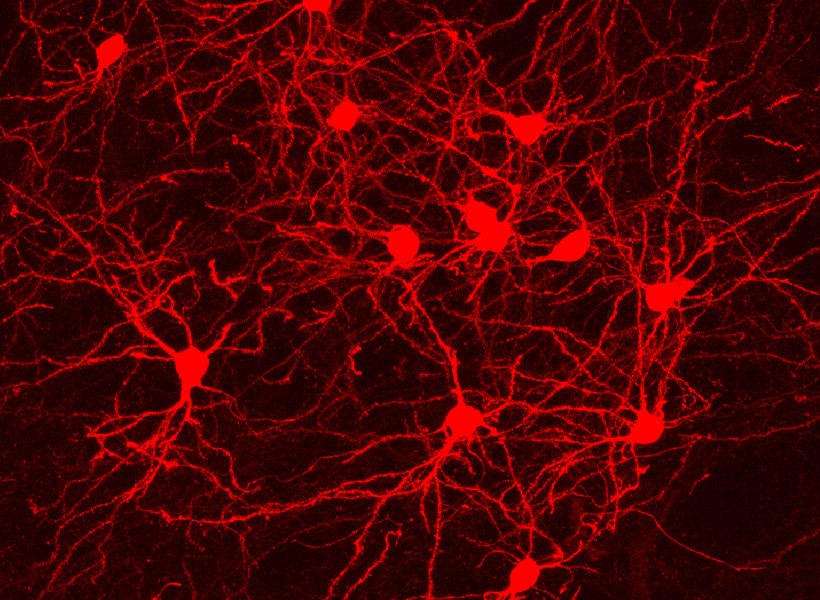
That means neuroscientists can now pair monosynaptic tracing with many of neuroscience’s most powerful tools for functional studies. To facilitate those experiments, Wickersham’s team encoded enzymes called recombinases into their connection-tracing rabies virus, which enables the introduction of genetically encoded research tools to targeted cells. After tracing cells’ connections, researchers will be able to manipulate those neurons, follow their activity, and explore their contributions to animal behavior. Such experiments will deepen scientists’ understanding of the inputs select groups of neurons receive from elsewhere in the brain, as well as the cells that are sending those signals.
Jin, who is now a principal investigator at Lingang Laboratory in Shanghai, says colleagues are already eager to begin working with the new non-toxic tracing system. Meanwhile, Wickersham’s group has already started experimenting with a third-generation system, which they hope will improve efficiency and be even more powerful.